AI and Data Protection Top 5: Volume 1, Issue 2
Summary of latest trends in AI governance and data protection. This issue covers EU AI Act, ToS updates for AI use, SEC cybersecurity updates, LLM compliance and Amazon Bedrock.

Welcome to the latest issue in a series covering top 5 recent trends at the intersection of AI governance and data protection. The purpose of this series is to keep technology and legal professionals up-to-date on the rapidly evolving developments in this space. Each issue will provide a summary of latest news on this topic, striking a balance between regulatory updates, industry trends, technical innovations, and legal analysis.
In this issue, we are covering the timeline of EU AI Act enforcement (2025-2027), best practices for ToS updates for AI use, SEC cybersecurity updates, LLM compliance benchmarks, and AI guardrails in Amazon Bedrock.
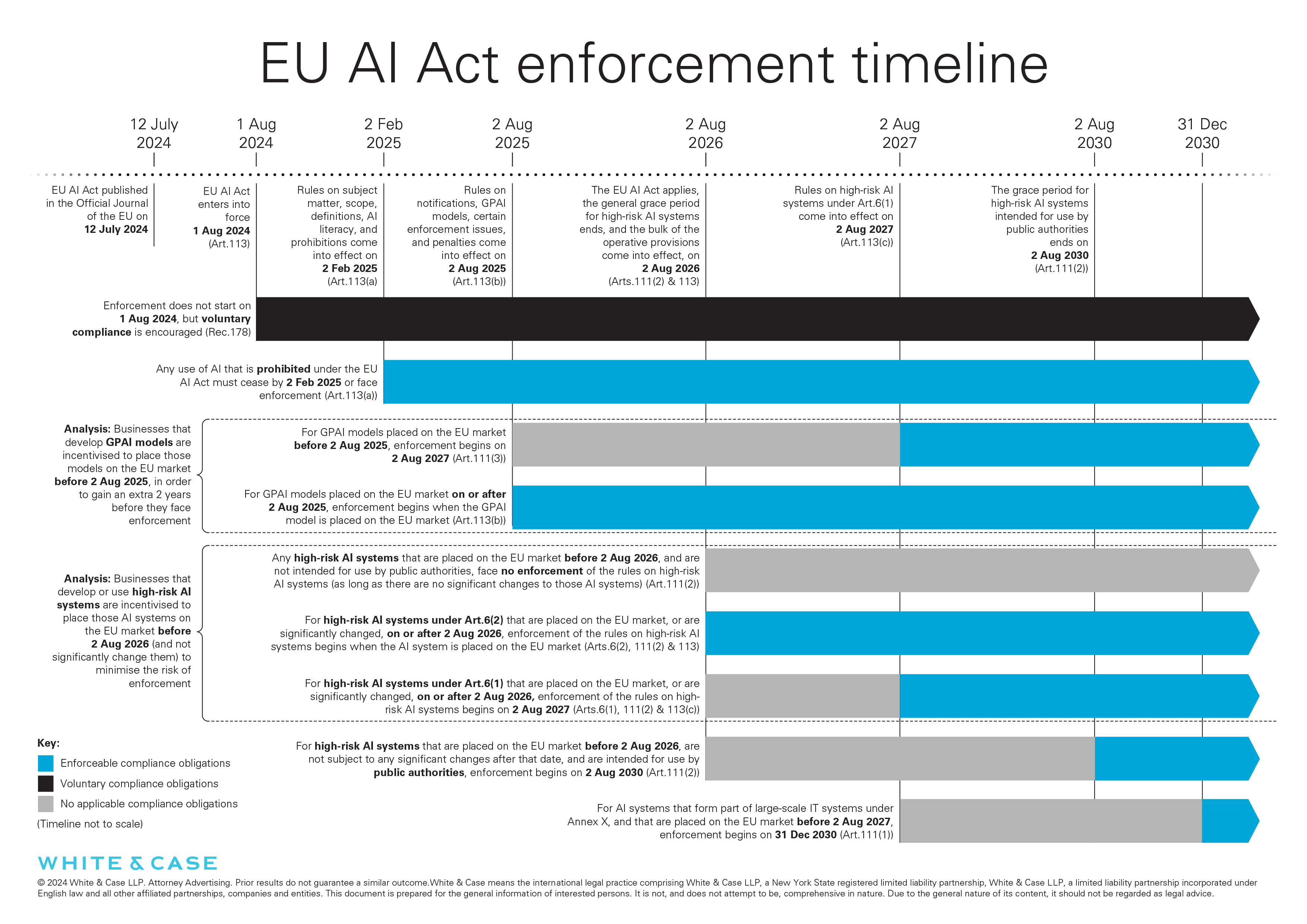
#1: EU AI Act Enforcement Timeline (2025-2027)
- The AI Act was published in the Official Journal of the EU on 12 July 2024. The deadlines for compliance, which all flow from 1 August 2024, come into force over the course of three years.
- Six months: 2 February 2025 – The ban on certain prohibited AI practices, as set out in Article 5 of the AI Act, will come into effect. This includes AI systems that are manipulative or deceptive, emotion inference systems or systems that exploit a person's vulnerability (among other things).
- One year: 2 August 2025 – The regime for general-purpose AI (GPAI) models comes into effect. It covers AI models that can perform a wide range of distinct tasks, such as generating text, audio, images or video, and can be integrated into AI systems that have an even wider functionality.
- Two years: 2 August 2026 – The regime for high-risk AI in Annex III and limited risk-AI comes into effect. Annex III systems include, among other things, workplace AI systems, AI used for safety in critical infrastructure, and AI used for biometric categorization based on sensitive data. Limited risk-AI (such as chatbots) must also comply with transparency obligations by this date.
- Three years: 2 August 2027 – The regime for high-risk AI that is integrated into products subject to the product safety regulations comes into effect.
Organizations should put together a compliance roadmap based on their risk-classifications and plan accordingly.
#2: ToS Updates for AI Use: Best Practices
- ToS updates about using AI are becoming more frequent as more organizations begin to integrate it in their products. However, lack of proper communication about AI use can result in confusion and outrage.
- One of the earliest example is Zoom, when the update to its Terms of Service created a controversy, in part due to mis-communication over user's ability to opt-out of using their data for training AI models.
- Earlier this year, Slack came under fire for a privacy policy update about using user data for AI training that was not clearly communicated.
- More recently, LinkedIn and Meta have needed to adjust the privacy practices in EU to ensure that users have the opportunity to opt-out of AI training.
To avoid these issues, organizations should clearly communicate what kind of user data (e.g., personal, aggregate, or anonymized) is used to train what kinds of models (e.g., general organization-wide or local customer-specific), whether they can opt-out of it, and for how long the data is retained.
#3: SEC Cybersecurity Updates
- Public companies subject to the SEC not only have to comply with the disclosures requirements under the new SEC cybersecurity rules but also ensure that their cybersecurity controls are meeting SEC requirements.
- Earlier this year, SEC charged R.R. Donnelley & Sons Co. with cybersecurity related controls violations relating to cybersecurity incidents and alerts in late 2021.
- Later in the year, SEC charged Unisys, Avaya, Checkpoint, and Mimecast with misleading cyber incident disclosures related to how they were impacted by the compromise of SolarWinds’ Orion software in 2020 and 2021.
- More organizations are filing 8-K disclosures for potential material cybersecurity incidents. For e.g., Dropbox filed an 8-K for an incident which it believed did not have or was not "reasonably likely to have, a material impact."
The new SEC rules and recent enforcement actions emphasize the importance of managing and reporting cybersecurity risk.
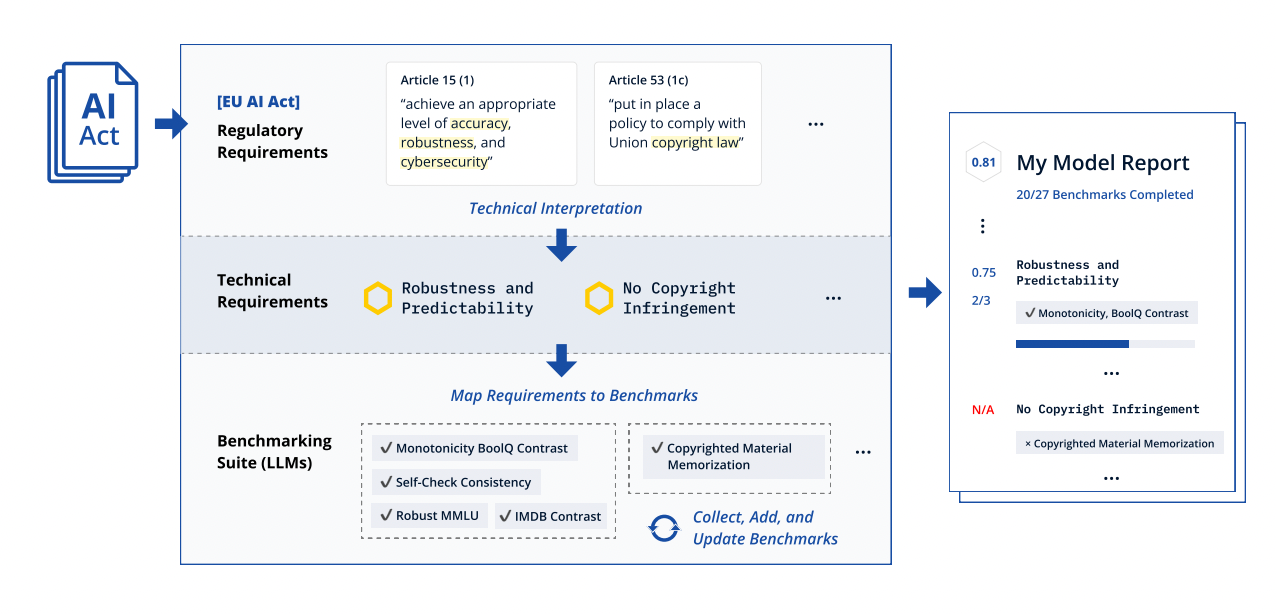
#4: LLM Compliance Benchmark: Research Findings
- The EU AI Act imposes specific requirements for General Purpose AI (GPAI) models. (Enforcement begins 2 August 2025, as noted above).
- A recent research study, using an open-source compliance framework, tested the GPAI models from big tech companies and awarded them a score between 0 and 1 across the various categories required for compliance with the EU AI Act.
- Models developed by Alibaba, Anthropic, OpenAI, Meta and Mistral all received average scores of 0.75 or above. "Claude 3 Opus", a model developed by Anthropic, received the highest average score, 0.89.
- The testing uncovered some models' shortcomings in key areas, spotlighting where companies may need to divert resources in order to ensure compliance. For e.g., discriminatory output been a persistent issue in the development of GPAI models, reflecting human biases around gender, race and other areas.
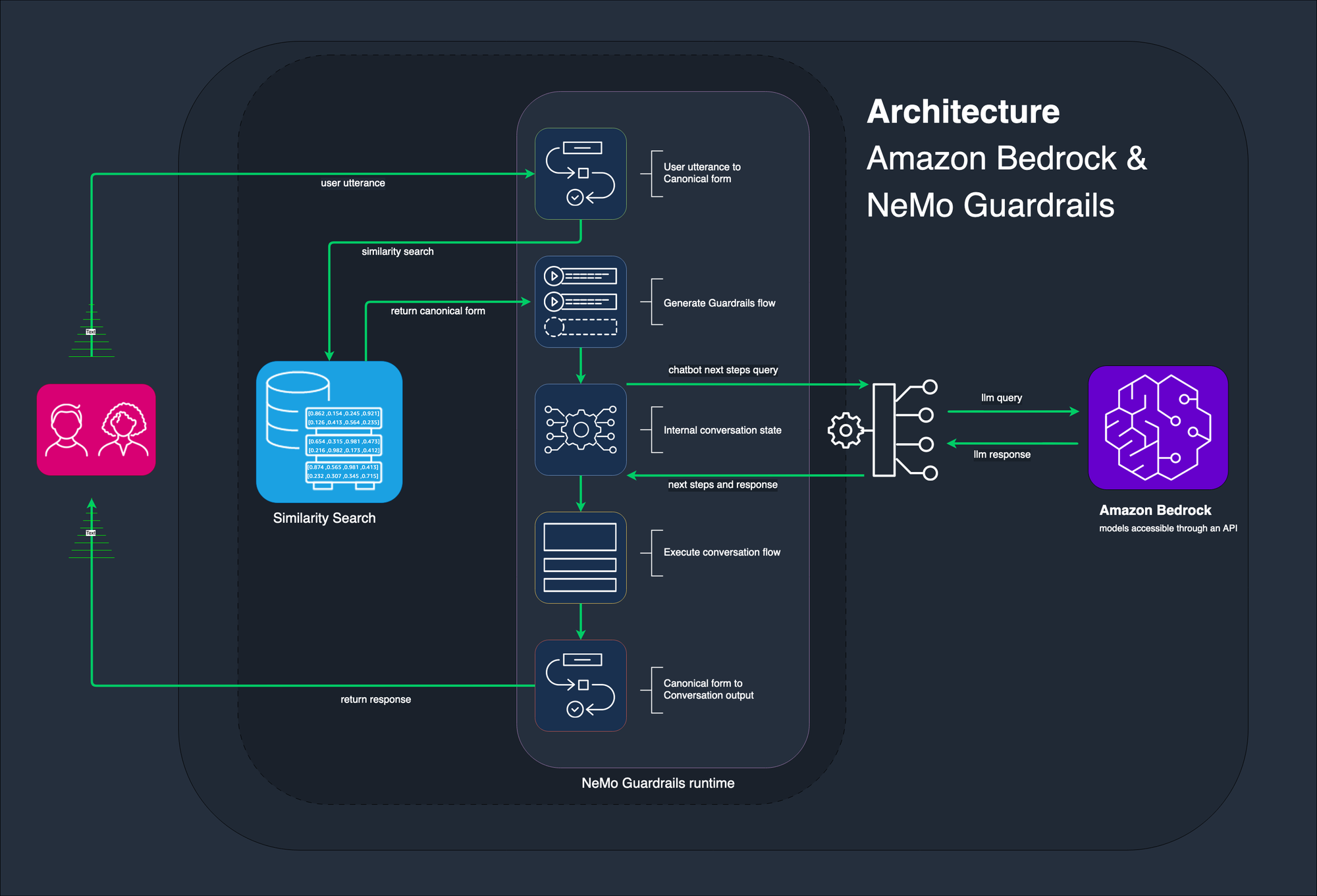
#5: AI Governance in Practice: Amazon Bedrock
AI governance requirements and regulatory guidance is only as helpful as the implementations to support them in mainstream products. The AI guardrails framework supported in Amazon Bedrock is a good step forward in this direction by a major vendor.
Below is the summary of capabilities:
- Bedrock Guardrails: Comprehensive and Customizable
- Features: Implements safeguards customized to specific use cases and responsible AI policies.
- Key Benefits:
- Denied Topics: Define topics to avoid using natural language descriptions.
- Content Filters: Set thresholds for filtering harmful content across categories like hate, insults, sexual, and violence.
- PII Redaction: Selectively redact personally identifiable information (PII) from responses.
- Integration: Can be applied to all large language models (LLMs) in Amazon Bedrock.
- NVIDIA's NeMo Guardrails - Tailored for Advanced Needs
- Jailbreaking Rail: Restricts AI from deviating from a set response format.
- Topical Rail: Ensures AI responses stay within the predefined topic.
- Moderation Rail: Moderates AI responses to maintain a neutral stance.
That's it for this issue. Subscribe to receive future issues directly in your inbox.
Previous Issues
Connect with us
If you would like to reach out for guidance or provide other input, please do not hesitate to contact us.
